Hydraulic Learning
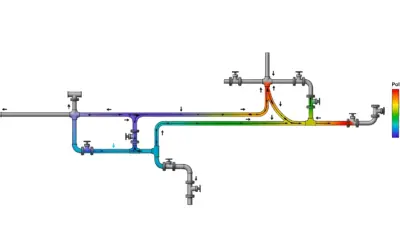
Pollutant Propagation in Pressurized Networks
[Exercise] Pollutant Propagation in Hydraulic Networks (US Units) DISCOVER MORE Optimal Control Valve Sizing & Placement Learn how to correctly size valves for efficiency. Pressure Profile Analysis Understanding hydraulic grade lines in systems. Sizing a Steel...
Optimal Control Valve Sizing & Placement
Exercise: Optimal Control Valve Placement Optimal Control Valve Sizing & Placement Context: Industrial Water Distribution System In pressurized hydraulic networks, the placement of a Control ValveA valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow...
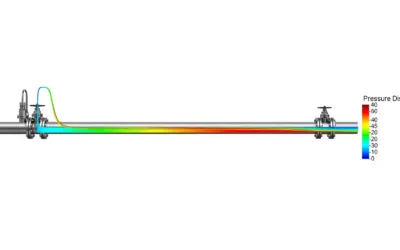
Pressure Profile Analysis
Pressure Profile in a Discharge Pipe Pressure Profile Analysis: Discharge Pipeline Context: Discharge PipelineA pipeline carrying pressurized fluid from a pump to a destination point. Design for a Water Supply System. You are a junior civil engineer tasked with...

Frequently Asked Questions - Hydraulics
Find answers to the most common questions about hydraulic systems here.
Hydraulics is a branch of science and technology concerned with the mechanical properties of liquids in motion or under pressure. In an industrial context, it refers to the use of pressurized fluids (usually oil) to generate, control, and transmit power. It's an effective way to multiply force for applications like presses, heavy machinery, or braking systems.
The main difference lies in the fluid used. Hydraulic systems use liquids (like oil), which are virtually incompressible. This allows them to transmit very large forces and position actuators with high precision. Pneumatic systems use a compressible gas (usually air). They are faster, cheaper, and cleaner, but cannot handle such heavy loads and offer less precision due to the compressibility of air.
A basic hydraulic circuit typically includes:
- A reservoir: to store the hydraulic fluid.
- A pump: to pressurize the fluid and make it circulate.
- A motor (electric or internal combustion): to drive the pump.
- Valves: to control the direction, pressure, and flow rate of the fluid.
- An actuator (cylinder or hydraulic motor): to convert hydraulic energy into mechanical work.
- Hoses and pipes: to transport the fluid between components.
- A filter: to remove contaminants from the fluid.
Oil (mineral or synthetic) is preferred for several reasons: it is virtually incompressible, ensuring excellent power transmission. Additionally, it lubricates the system's moving parts (pump, cylinders), protects components from corrosion, and helps dissipate the heat generated by the system's operation.
Hydraulic Press Simulator
Use the slider to increase pressure and drag on the scene to rotate.

About Us
During our studies, we quickly realized it was difficult to find practice problems covering every field of hydraulics. We felt we needed to solve this problem to improve comprehension of the coursework, and that’s how Hydraulic Learning was born.


Hydraulic Learning

Fundamentals of Hydraulics
Pipe Flow (Circuits & Networks)
Oil Hydraulics (Hydraulic Power)
Practice Problems
Pollutant Propagation in Pressurized Networks
[Exercise] Pollutant Propagation in Hydraulic Networks (US Units) DISCOVER MORE Optimal Control Valve Sizing & Placement Learn how to correctly size valves for efficiency. Pressure Profile Analysis Understanding hydraulic grade lines in systems. Sizing a Steel...
Optimal Control Valve Sizing & Placement
Exercise: Optimal Control Valve Placement Optimal Control Valve Sizing & Placement Context: Industrial Water Distribution System In pressurized hydraulic networks, the placement of a Control ValveA valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow...
Pressure Profile Analysis
Pressure Profile in a Discharge Pipe Pressure Profile Analysis: Discharge Pipeline Context: Discharge PipelineA pipeline carrying pressurized fluid from a pump to a destination point. Design for a Water Supply System. You are a junior civil engineer tasked with...
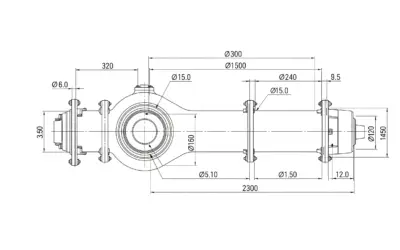
Sizing a Steel Penstock for Hydropower
Penstock Sizing - Pressurized Hydraulics Sizing a Steel Penstock for Hydropower Context: Pressurized HydraulicsBranch of fluid mechanics dealing with confined liquid flow under pressure, typical in pipes. and PenstockA conduit or pipe that carries water from a...
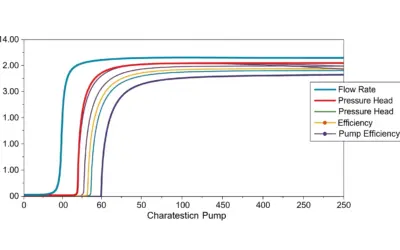
Study of a Centrifugal Pump Characteristic Curve
Hydraulic Pump Characteristic Curve Study Study of a Centrifugal Pump Characteristic Curve Context: Fluid MechanicsThe branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them. and TurbomachineryMachines that...
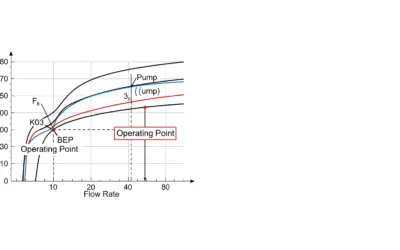
Centrifugal Pump Analysis
Hydraulic Systems: Pump Operating Point Analysis Centrifugal Pump Analysis: Determining the Operating Point Context: Hydraulic Network AnalysisThe study of flow and pressure distribution in piping systems.. In industrial and civil engineering applications, selecting...
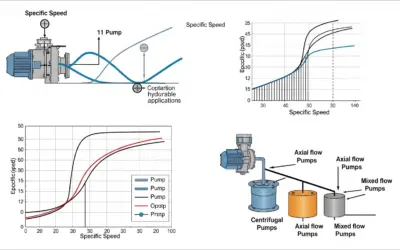
Pump Specific Speed Calculation
Pump Specific Speed Calculation (Hydraulics) Pump Specific Speed Calculation (\(N_{\text{s}}\)) Context: Specific Speed (\(N_{\text{s}}\))A dimensionless index (in theory) but dimensioned in US Practice, used to classify pump impellers based on their shape and...
Pressure Drop in a Proportional Directional Valve
Hydraulic Proportional Valve Exercise Pressure Drop in a Proportional Directional Valve Context: Fluid Power SystemsTechnology that deals with the generation, control, and transmission of power using pressurized fluids.. In modern hydraulic circuits, Proportional...
Hydraulic Glossary
Explore the principles and components of fluid mechanics.
Term Index
Select a Term
Click a word in the index to display its detailed definition here.